Diltiazem
Diltiazem dosages: 180 mg, 60 mg
Diltiazem packs: 30 pills, 60 pills, 90 pills, 120 pills, 180 pills, 270 pills, 360 pills
Purchase diltiazem 180mg online
Areas like this have been mistaken in some circumstances for Hassall corpuscles, leading to an incorrect analysis of lymphocyte-rich thymoma. Hyalinization of Follicle Dysplastic Dendritic Cells in Follicle (Left) Abnormal, dysplastic follicular dendritic cells are seen in a burned-out follicle in Castleman disease of the mediastinum, hyaline-vascular sort. Dysplastic or atypical dendritic cells may be discovered within the follicles or within the interfollicular areas of the nodes and should give rise to dendritic cell sarcomas. Dendritic Cells: High Power Focus of Kaposi Sarcoma (Left) Castleman illness of the mediastinum shows a focus of Kaposi sarcoma within the interfollicular areas arising in association with Castleman illness. Notice the abnormal follicle on the backside with a hyalinized vessel traversing the mantle zone into the germinal center. Interfollicular Plasmacytosis Interfollicular Plasmacytosis: High Power (Left) Scanning magnification in Castleman disease, plasma cell type, shows 2 small, burned-out follicles with hyalinized germinal centers and onion pores and skin mantle zones surrounded by a dense plasma cell population in the interfollicular areas. Plasma Cell Type Stroma-Rich Variant (Left) Castleman illness, plasma cell type, reveals an atrophic, burned-out follicle with a hyalinized germinal middle containing a sclerosed vessel. Notice sheets of monotonous mature plasma cells in the interfollicular areas and absence of mantle zone lymphocytes. Presence of Cartilage Attenuated Epithelium (Left) Bronchogenic cyst shows respiratory epithelium margin with areas of fibrosis. Weissferdt A et al: Cystic well-differentiated squamous cell carcinoma of the thymus: a clinicopathological and immunohistochemical study of six circumstances. Histopathologic evaluation of the cyst lining is required to establish the proper prognosis. Presence of Cartilage Respiratory Epithelium (Left) Higher magnification of a bronchogenic cyst shows cartilage and a cystic construction lined by a respiratory kind of epithelium. Bronchial Glands Endobronchial Glands (Left) Bronchogenic cyst shows regular endobronchial glands in the walls of the cystic buildings. The lining is a low sort of cuboidal epithelium, and these findings are in keeping with a mesothelial cyst. Cuboidal Epithelium Flattened Epithelium (Left) this mesothelial cyst consists of flattened epithelium with out atypia and underlying fibroconnective tissue with minimal inflammatory changes. In addition, the cyst seems uniloculated and lined by a flattened type of epithelium. Residual Thymus Residual Thymus (Left) High magnification exhibits a mediastinal cyst with obvious presence of thymic tissue and a cystic structure lined by a flattened sort of epithelium. Enteric Epithelium Gastric Type of Epithelium (Left) Enteric cyst reveals the cystic structure lined by enteric, mucinous kind of epithelium. Cystic Changes Inflammatory Reaction (Left) Enteric cyst shows cystic modifications throughout the wall of the cyst. Note the presence of mucinous contents along with the mucinous epithelium lining the cystic structure. Histologic Appearance Cystic Hassall Corpuscles (Left) Cystic dilatation of Hassall corpuscles is a common function in acquired multilocular thymic cysts. The lining of the cyst is often seen to be in continuity with residual Hassall corpuscles in the partitions of the cysts. This is most likely going due to rupture of the cysts with hemorrhage and extrusion of epithelial cells into the stroma eliciting an inflammatory response. Izumi H et al: Multilocular thymic cyst associated with follicular hyperplasia: clinicopathologic research of 4 resected cases. The cysts range in measurement and shape, and some of the bigger cysts seem to result from the confluence of smaller cysts. Cystic Spaces With Chronic Inflammation Cystic Space (Left) A multilocular thymic cyst shows a quantity of irregular cystic spaces lined by epithelium and containing proteinaceous debris in their lumina. The cyst wall is lined by a thin layer of cuboidal epithelium and is surrounded by dense inflammatory infiltrate composed primarily of small lymphocytes and admixed with occasional plasma cells and histiocytes. Cyst Wall With Inflammation Cyst Wall With Inflammation (Left) Wall of a cyst in a patient with a multilocular thymic cyst exhibits polypoid protrusion into the lumen by epithelium-lined stroma with features of granulation tissue.
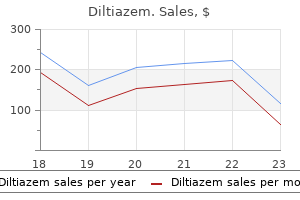
Buy diltiazem 180 mg cheap
Surgical Approach With the patient in a supine place, the stomach is explored by a median laparotomy after a normal mixture of an antibiotic single shot has been given. The primary tumor is mobile, and at the peritoneal reflection, a careful palpation of the colon reveals no synchronous second colon neoplasm and no evidence of peritoneal carcinomatosis. No lymph node involvement is grossly suspected, particularly not at the root of the inferior mesenteric artery or along the aorta. In the United States, the usual management entails adjuvant 5-fluorouracil-based chemoradiation. In addition to the lymph node involvement, the poor differentiation of the tumor and the microscopic invasion of veins are danger elements for tumor recurrence. In Europe, adjuvant radiotherapy will not be supplied if a complete mesorectal excision and an R0-resection have been achieved in rectal cancer of the higher third of the rectum. Complete colonoscopy ought to be carried out 3 months after the initial surgical procedure to exclude further neoplastic lesions. Tumor (Tu) has infiltrated via all layers of the colonic wall and into the perirectal fats tissue. Left hemicolon with a quantity of small tubulovillous adenomas (low grade) and minor diverticular illness are noted. Total mesorectal excision preserves male genital function compared with conventional rectal most cancers surgery. Nelson H, Petrelli N, Carlin A, et al, for the National Cancer Institute Expert Panel. Digital rectal examination is painful, and allows detection of a strong and glued rectal mass 4 cm above the anal verge. Anal sphincter pressures at rest and underneath squeezing are clinically inside the regular range. Any suspicion must be verified by genetic testing of the affected person and, if genetic testing outcomes are optimistic, all first-degree relatives. The consequence of a positive genetic test in family members is colonoscopy starting at the age of 25 and repeated inside brief intervals (1 to 2 years). In distal rectal carcinoma, changes in stool kind, anorectal tenesmus, or painful defecation are typical. Other signs such as pelvic or again pain, malaise, or complete mechanical obstruction are much less frequent and sometimes indicate advanced illness. Digital rectal examination is the initial diagnostic device and is crucial to estimate tumor dimension, location, and relation to the surrounding constructions such as the sphincter muscle. Rigid or versatile proctosigmoidoscopy is used to visualize the tumor, to take biopsies for histologic confirmation of the suspected analysis, and to give an correct measurement of the gap of the tumor from the anal verge. However, the liver can be evaluated successfully with intraoperative ultrasound. In many sufferers, hemorrhoidal disease may be found to be the source of bleeding, with constipation having developed secondary to painful defecation. Recommendation Biopsies of the first tumor ought to be sent for histologic analysis. Complete versatile colonoscopy must be performed to exclude a synchronous secondary colon most cancers. Case Continued Histology of the biopsies of the rectal major reveals reasonably differentiated carcinoma of the rectum. Colonoscopy reveals a polypoid, partially ulcerated tumor that includes one third of the rectal circumference and is located on the left facet. No evidence of tumor unfold into the prostate, vesicles, pelvic floor, or anal sphincter. To supply a sphincter-sparing method to the rectal most cancers, the affected person is introduced with the choice of neoadjuvant chemoradiation therapy over 6 weeks (50. The just lately revealed randomized German rectal most cancers trial evaluating the standard U. Although the hypofractionated 1-week schedule of irradiation (5 5 Gy over 1 week) with immediate surgical procedure is the favorite preoperative therapy in Europe, on this case we determined to choose a traditional lengthy irradiation protocol (50. At the extent of the vesicles (V), distal rectal tumor (Tu) with tumor infiltration into the mesorectum, on the left-hand side close to the mesorectal fascia (visceral fascia of the pelvis).
Buy diltiazem online
Primary postpartum hemorrhage is outlined as the hemorrhage that occurs within 24 hours following delivery of the infant. Obstetric hemorrhage is the main cause of maternal deaths in each developed and creating nations. To alert obstetric and anesthetic seniors and the on-duty midwife (call for help). What are the different surgical measures that may be taken to control the hemorrhage It is done through the use of different types of hydrostatic balloon catheter (Foley catheter, Bakri balloon. Uterine devascularization procedures: (a) Bilateral ligation of uterine or utero-ovarian vessels. However, balloon tamponade and hemostatic suturing methods are less complicated and much easier to carry out. Time of onset of occasions, time of begin of therapy to report the category of employees involved, scientific situation of the affected person, monitoring parameters, management points are all docuemented. Other causes not associated to being pregnant: (i) Cervical pathology-cervical ectopy, polyp or malignancy. Spontaneous abortion or miscarriage could also be additional classified into: (a) threatened, (b) inevitable, (c) full, (d) incomplete, (e) missed and (f) septic. When the process of miscarriage has started however continuation of pregnancy remains to be potential. Clinically the patient presents with (a) bleeding per vaginam, (b) pain in the decrease abdomen, (c) on speculum examination, slight bleeding from the exterior os and (d) on pelvic examination, uterine size corresponds to the period of amenorrhea. There is discrepancy between gestational sac growth and the embryonic development. It is a clinical sort of miscarriage the place the abortion course of has progressed to a state wherefrom continuation of pregnancy is impossible. Clinically the patient presents with (a) elevated vaginal bleeding, (b) increased decrease abdominal pain, (c) on internal examination: inner os is dilated, via which the merchandise of conception may be felt. Suction evacuation or dilation and evacuation followed by curettage is completed under general anesthesia. When the fetus is dead and is retained contained in the uterus for a variable time frame. Any abortion process when difficult with options of infection (sepsis) of its contents either local (uterus) or systemic is called septic abortion. Three or extra consecutive miscarriages (spontaneous abortions) before 20 weeks of pregnancy, in a woman, are outlined as recurrent miscarriage. Three or extra consecutive spontaneous abortions (miscarriages) earlier than 20 weeks are defined as recurrent miscarriage. Autosomal trisomies are the commonest of abnormalities found in the aborted fetuses. All Rh-negative women with vaginal bleeding in early pregnancy (miscarriage or ectopic pregnancy) should receive anti-D immunoglobulin. Evacuation of the uterus as early as possible is completed to remove the retained merchandise of conception Suction evacuation or dilatation and evacuation of the uterus. May need laparotomy Threatened abortion Incomplete abortion Missed abortion Fetus is dead and is retained contained in the uterus for a variable time frame Inevitable abortion Process of abortion is related to cervical dilatation and effacement. Gravida denotes a pregnant state, both present and previous, regardless of interval of gestation Q. During contraction, the transverse diameter of the uterus is reduced but the longitudinal diameter increases d. Measurement of brachial artery pressure reflects the strain in the uterine artery d. Visualization of inner cervical os is extra accurate with transabdominal than with transvaginal sonography b. It helps sperm transport to the fallopian tube from the vagina within two minutes (hypermotility) Q.
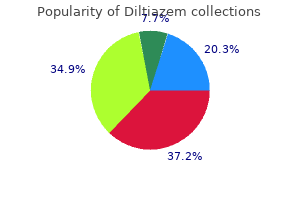
Buy diltiazem toronto
Screening of cervical cytology by automated microscope with digital camera and evaluate by expert cytopathologist is done. Women having both the check results adverse, the test interval elevated by greater than 3 years. Results are analysed: (a) Both the results adverse Routine screening yearly is completed. A younger girl who has not menstruated by sixteen years of age (16th birth day) is taken into account primary amenorrhea. Physiological: (a) Before puberty, (b) following menopause, (c) throughout pregnancy and (d) during lactation. Pathological: (a) Cryptomenorrhea, (b) main amenorrhea, (c) secondary amenorrhea. Absence of menstruation for six months or more in a girl who has menstruated normally in the past. Ovarian components: (i) Polycystic ovarian syndrome, (ii) Premature ovarian failure, (iii) pelvic radiation and (iv) bilateral oophorectomy three. Iatrogenic: Drugs-Antihypertensives (reserpine), psychotropic (phenothiazines), tricyclic antidepressants. What is the importance of adverse result of estrogen-progesterone challenge take a look at What other exams ought to be performed for a lady with amenorrhea (with normal anatomical tract), who had no bleeding on progesterone challenge test However, if the girl is found seropositive and desires to continue being pregnant, a number of steps are taken to reduce the unfold of the an infection as minimum to the fetus, neonate and the others in the society (health care staff). However well being consciousness applications and follow of safer sex are the other important steps. These are: vasomotor (hot flush), genital and urinary symptoms (atrophic modifications, dyspareunia and dysuria), psychological (anxiety, temper swing, insomnia, irritability, depression), osteoporosis and fracture of bones, cardiovascular (coronary artery disease) and cerebrovascular illness. Menopause may be either natural (normal) with age or irregular: (i) premature or (ii) artificial-surgical or radiation induced. These are: improvement of vasomotor signs, urogenital atrophy and bone mineral density. The risks are: breast most cancers, endometrial most cancers, venous thrombo-embolism, coronary artery illness and altered lipid metabolism. These are: undiagnosed genital tract bleeding, estrogen dependent neoplasm in the physique, lively liver and gallbladder illness and history of thromboembolism. This group contains women with premature ovarian failure, gonadal dysgenesis and ladies with surgical or radiation menopause. However there are tons of nonhormonal strategies of therapy that can be used for the problems of menopause. Changes in lifestyle, exercise, intake of calcium and vitamin D are found helpful within the management of menopause. In the evaluation of feminine infertility each the laparoscopy and hysterosalpingography are used primarily for the detection of the patency of the fallopian tubes. Chromopertubation is helpful to study the nature of tubal motility in addition to tubal patency. Therefore laparoscopy helps to evaluate the pelvic, ovarian and the peritoneal factors for infertility apart from that of tubal patency. These pathologies are often thought of as the important female elements for infertility. Laparoscopic electrofulguration of pelvic endometriotic implants is finished to improve fertility as properly as to improve the symptoms of pelvic ache in ladies. Choriocarcinoma is a highly malignant tumor arising from the chorionic epithelium. Chemotherapy is the mainstay in the remedy as chemotherapy is found to be highly effective. Methotrexate has many unwanted effects affecting the gastrointestinal, hemopoietic and different techniques. Drugs combined in this protocol are etoposide, methotrexate, actinomycin D, cyclophosphamide, vincristine and folinic acid. Young women can have being pregnant 1 12 months after profitable completion of chemotherapy. Primary hysterectomy has obtained a restricted place until the tumor is discovered resistant to chemotherapy. Considering all the advantages and its high efficacy, chemotherapy is considered the mainstay in the remedy of choriocarcinoma.
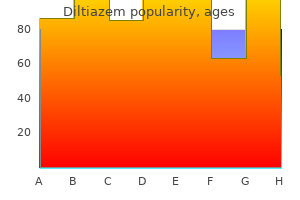
Order diltiazem cheap online
It is the replacement of squamous epithelium of the ectocervix by columnar epithelium of endocervix by the process of metaplasia. It must be used solely when the operation is finished beneath basic or regional anesthesia because the instrument is heavy. A second layer of (musculofascial) suture with the same material is used to reinforce the primary layer. It was initially a gentle rubber catheter with a balloon sleeve of rubber across the shaft beneath the attention of the catheter. Currently, the catheter is made from latex which is much less irritating to urethral mucosa. To assess the patency of the fallopian tube throughout laparotomy, catheter is launched within the uterocervical canal (vaginally) and the balloon is inflated then dye is pushed. To dilate the cervix to facilitate drainage of intrauterine collection - pyometra, hematometra or lochiometra. Ans: (a) Senile endometritis (b) Endocervical carcinoma (c) Tubercular endometritis (d) Infected lochiometra (obstetrical). To maintain the fundus of the uterus and to give traction while the clamps are positioned during whole belly hysterectomy for benign lesion. Usually the anterior lip is held in circumstances like D and C, D and E, but in some situations, the posterior lip is to be held. Such conditions are: (a) During amputation of cervix or vaginal hysterectomy when the posterior cervico-vaginal mucous membrane is incised. Ans: Subtotal hysterectomy is finished in sure conditions the place total hysterectomy Self-assessment 484 Bedside Clinics and Viva-Voce in Obstetrics and Gynecology is discovered to be difficult or time-consuming. Difficult tubo-ovarian mass with obliteration of the anterior and posterior pouches. In non descent vaginal hysterectomy as a substitute for laparoscopic hysterectomy. To detect evidence of ovulation-by seeing the secretory changes in the endometrium. Cervical mucus research: Disappearance of fern sample beyond 22nd of the cycle suggests ovulation. Vaginal cytology: Maturation index shifts to the left due to the effect of progesterone. Serum Progesterone: A rise in serum levels of progesterone within the secretory section of the cycle (D-21) when compared to D-8 of the cycle suggests ovulation 5. To plug the uterine cavity with gauze twigs in continued bleeding after removal of polyp. Uses To remove the merchandise of conception in D and E after its separation partially or utterly. The products are caught and then with twisting movements and simultaneous traction, the products are eliminated. Dangers: It might produce injury to the uterine wall to the extent of even perforation. Not occasionally, a section of intestine or omentum could even be pulled out by way of the hire. This forceps is used to maintain soft tissues for a protracted time with minimal tissue harm. Uses To maintain the margins of the vaginal flaps in colporrhaphy operation To hold the peritoneum or rectus sheath during restore of the belly wall To maintain the margins of the vagina in stomach hysterectomy To hold the anterior lip of the cervix in D and C operation To catch the torn ends of the sphincter ani externus in full perineal tear restore To remove a small polyp To take out the tissue in wedge biopsy. The widespread symptoms are genital organs protruding out of the vaginal opening, problem in strolling, sitting, urination or defecation. Prolapse might interfere with sexual activity or could cause vaginal bleeding as a result of ulceration of mucosa. Uses To repair and regular the uterus when conservative surgery is completed on the adnexae (tuboplasty operation). Cervix is occluded with the instrument and methylene blue dye is injected into the uterine cavity by way of the fundus utilizing a syringe and a needle. Important concerns before myomectomy (prerequisites of myomectomy) Submucosal polyp, submucous fibroid, any tubal block or endometrial carcinoma should be excluded earlier than performing myomectomy. History: Bonney, William Francis Victor (1872-1953): Gynecologist at the Middlesex and Chelsea Hospitals, London.
Syndromes
- Effectiveness -- How well does the method prevent pregnancy? Look at the number of pregnancies in 100 women using that method over a period of 1 year. If an unplanned pregnancy would be viewed as potentially devastating to the individual or couple, a highly effective method should be chosen. In contrast, if a couple is simply trying to postpone pregnancy, but feels that a pregnancy could be welcomed if it occurred earlier than planned, a less effective method may be a reasonable choice.
- Anesthesia
- Learn why you keep having repeated bladder infections
- Regular vigorous exercise
- Abnormal heartbeat or heart sounds (murmurs, extra heart sounds)
- Balance problems
- Peripartum cardiomyopathy
- Wash hands often with soap and water for 15 - 20 seconds, especially after you cough or sneeze. You may also use alcohol-based hand cleaners.
Discount generic diltiazem canada
The chondrocytes are often arranged in clusters, located in lacunar spaces inside pale blue hyaline matrix and have uniform round nuclei and plentiful eosinophilic cytoplasm. Sugiura Y et al: Convexity dural chondroma: a case report with pathological and molecular evaluation. It appears as granular basophilic stippling of the matrix, which often surrounds individual chondrocytes to form a reticular pattern. Dense Calcification Granulomatous Inflammation and Giant Cells (Left) this medium-power micrograph depicts very dense mineralization of the cartilage matrix consisting of coarse, basophilic particles of calcium. This micrograph illustrates epithelioid macrophages and osteoclastic large cells in a calcified tumor. Xanthogranulomatous Inflammation Ossification (Left) Xanthogranulomatous inflammation may be present in gentle tissue chondroma, consisting of sheets or clusters of foamy histiocytes. When in depth, such a tumor can be mistaken for fibrous histiocytoma or tenosynovial large cell tumor. It may be situated both at the heart or periphery of the tumor and is formed via endochondral ossification of calcified cartilage matrix. Soft tissue chondroma has a predilection for the palms and feet, often close to a joint or tendon. Lobular Architecture and Calcification Calcified Cartilage Matrix (Left) this high-power micrograph of a densely calcified tumor depicts finely granular and coarse calcium deposits. The hyaline matrix is degenerated and the chondrocytes are not contained inside lacunae. Myxoid Matrix Stellate and Chondroblastoma-Like Cells (Left) In myxoid areas, the chondrocytes lose their lacunae and assume stellate shapes and rounded cells that resemble chondroblasts with ample eosinophilic cytoplasm and eccentric grooved or reniform nuclei. Fibrocollagenous Matrix 482 Soft Tissue Chondroma Chondro-Osseous Tumors Circumscription and Lobular Architecture Calcification and Increased Cellularity (Left) Soft tissue chondroma is well circumscribed and properly demarcated from adjacent soft tissues. It sometimes has a multilobular structure, as proven, and zones of calcification. The mobile space is comprised by a combination of chondrocytes devoid of lacunae and mononuclear inflammatory cells and resembles tenosynovial large cell tumor. This high-power micrograph illustrates chondrocytes with nuclear enlargement and pleomorphism, which out of context could be suspicious for chondrosarcoma. Chondroblastoma-Like Features Cystic Degeneration (Left) this closely calcified delicate tissue chondroma incorporates cells with plentiful eosinophilic cytoplasm and eccentric nuclei with reniform and grooved shapes, resembling the cells of a chondroblastoma. Radiology High-Power Features (Left) the proliferating cells are benign-appearing chondrocytes with uniform small nuclei located inside lacunar spaces. Note the clustered association of the cells and occasional lacunae containing 2 cells. Note the overlying synovial membrane and nodules of cartilage with sharp borders, separated by fibrovascular tissue. Subsynovial Location Hyaline Cartilage Matrix and Cell Clusters (Left) In most circumstances of synovial chondromatosis, the matrix consists of pale blue or pink hyaline cartilage and the chondrocytes are organized in small clusters, as shown. Unlike the osteocartilaginous free bodies associated with degenerative joint disease, they lack concentric laminations and preserve the clustered arrangement of chondrocytes. Intraarticular Loose Bodies Calcification (Left) Calcification is widespread in synovial chondromatosis, as depicted. Endochondral Ossification 486 Synovial Chondromatosis Chondro-Osseous Tumors Cytological Atypia Synovial Chondromatosis of the Hip (Left) Degenerative cytological atypia may be seen in synovial chondromatosis. This high-power micrograph depicts large chondrocytes with eccentric cytoplasm and pleomorphic nuclei with smudged chromatin. Gross Appearance Nodules Separated by Fibrous Stroma (Left) this gross photograph depicts tissue eliminated at knee synovectomy. Note the attribute multinodular appearance as well as the means it studs the synovial membrane. In this location, synovial chondromatosis presents with ache, swelling, and deviation. It is histologically similar to skeletal osteosarcoma, consisting of irregular lace-like osteoid matrix and highgrade malignant cells with brisk mitotic exercise. Radiographic Appearance Malignant Bone Formation (Left) Most extraskeletal osteosarcomas are high-grade sarcomas and are characterised by direct production of malignant osteoid and bone by the neoplastic cells. It depicts classical features of osteosarcoma comprised by stable sheets and lace-like configurations of osteoid and large, pleomorphic spindle cells arranged in fascicles and storiform arrays.
Buy generic diltiazem 60 mg
Circumferential dissection is performed, and the wire is rigorously brought out by way of the main incision. Once resected, the specimen is oriented for the pathologists with sutures, and is first sent to radiology for a specimen radiograph to verify complete resection of the lesion. Some surgeons routinely take shave biopsies from all 4 quadrants of the cavity as well as a deep margin. Small titanium surgical clips are then positioned within the lumpectomy website to delineate the world for subsequent radiotherapy. Specimen mammography reveals that each one clustered microcalcifications have been 252 eliminated. Case 57 tient would have averted an axillary lymph node dissection and its attendant potential complications. Recommendations the choices at this juncture include present process a reexcision, though with widely optimistic margin the success of breast conservation is unlikely. The different alternative is to perform both a regular whole or a skin-sparing mastectomy, with or with out reconstruction, relying on the desires for the affected person. To enable symmetry, further interventions are often required on the contralateral breast. The affected person due to this fact must remember that choosing reconstruction often includes present process further surgical procedures. If the extensive native excision had shown evidence of an invasive element, then a sentinel node biopsy would be provided. The household practitioner referred the patient to your breast clinic for additional analysis. History reveals no particular breast complaints or symptoms, previous surgery, or mammographic screening. The areola feels considerably indurated with none lumps or firm tissues within the retroareolar area. The remaining breast tissue is unremarkable without suspicious enlarged axillary lymph nodes. Patients present clinically with eczematous modifications of the nipple often associated with itching, ulceration, and bleeding. Histologically, Paget disease is characterized by intraepidermal spread of huge spherical or ovoid tumor cells with abundant pale cytoplasms and huge pleomorphic and hyperchromatic nuclei with distinguished Differential Diagnosis Paget disease of the nipple is suspected. Nipple adenoma, papillomatosis, invasive ductal carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, eczema of the nipple, and 253 254 nucleoli. Regarding the exact origin of these Paget cells, at present most authors postulate the epidermotropic principle, which assumes that Paget cells are ductal carcinoma cells that have migrated from the underlying mammary ducts to the dermis of the nipple. Spot magnification view of the retroareolar area could also be useful for improved definition of the extent Case 58 of microcalcifications. If that is encountered, ultrasound-directed core biopsies ought to be taken to confirm this suspicion. A magnification view of the retroareolar area confirms the three or 4 microcalcifications without indicators of further extension. Surgical Approach the resection could be carried out with basic anesthesia or with native anesthesia and sedation. After hemostasis is achieved, the skin is closed intracutaneously with absorbable material. The postoperative course is uneventful and the affected person is discharged residence the same day. Case Continued the affected person receives radiation remedy to the breast in two tangential fields, in 25 fractions of 2 Gy delivered in 5 weeks, for a complete dose of fifty Gy. Apart from some redness of the pores and skin on the finish of the radiotherapy course, the remedy is uneventful. Four years later, the patient is freed from disease and without abnormality on bodily examination and mammography. Once invasive most cancers is suspected or confirmed, the 256 invasive lesion could also be much more intensive, and axillary lymph node involvement is seen in over half of the sufferers. In sufferers with Paget disease related to invasive cancer, a modified radical mastectomy remains to be thought-about commonplace treatment.
Cheap diltiazem 180mg without a prescription
Sawahata M et al: An epidemiological perspective of the pathology and etiology of sarcoidosis. Notice a few of the granulomas are in shut proximity to the bronchial submucosa, which accounts for the excessive diagnostic yield on bronchoscopic biopsies. Small Coalescing Granulomas Fibrosis Surrounding Granuloma (Left) Higher magnification of epithelioid granulomas in pulmonary sarcoidosis shows a concentric rim of fibrosis surrounding one of the granulomas. Notice the sparse inflammatory cells scattered in the interstitium outdoors of the granulomas. Sclerotic Granuloma Epithelioid Granuloma With Giant Cell (Left) Higher magnification of an epithelioid granuloma in pulmonary sarcoidosis reveals a concentric association of epithelioid histiocytes around a large multinucleated big cell with abundant eosinophilic cytoplasm. The asteroid bodies are made up of crystals situated inside the cytoplasm of the giant cells. Asteroid Body 432 Sarcoidosis Lung: Nonneoplastic and Systemic Conditions Confluent Granulomas With Fibrosis Extensive Stromal Hyalinization (Left) Confluence of granulomas in pulmonary sarcoidosis may result in the formation of a large nodular mass that may be confused radiologically for malignancy. Scattered Multinucleated Giant Cells Massive Stromal Sclerosis (Left) Higher magnification of nodular sarcoidosis of the lung shows extensive sclerosis and hyalinization of the stroma with scattered multinucleated big cells. The small scattered epithelioid granulomas are better appreciated at this magnification. The peribronchial location makes it very simple to identify the granulomas on endoscopic biopsies. Carney J et al: Aluminum-induced pneumoconiosis confirmed by analytical scanning electron microscopy: a case report and evaluation of the literature. Organizing Pneumonia-Like Areas Interstitial Fibrosis (Left) Areas of discrete interstitial fibrosis are present. Also notice the scattered multinucleated giant cells as nicely as a small lymphoid combination. Collections of Macrophages Scattered Giant Cells (Left) Areas with extra discrete fibrosis and collections of intraalveolar macrophages could be recognized. Peribronchial Fibrosis 436 Hard Metal Pneumoconiosis Pneumonitis Lung: Nonneoplastic and Systemic Conditions Inflammatory Changes Prominent Scarring (Left) Hard metallic pneumonitis reveals lung parenchyma with marked inflammatory changes and hyperplastic modifications of the bronchial and alveolar lining, in addition to accumulation of macrophages and big cells. Intravascular Macrophages Replacement of Normal Lung Parenchyma (Left) Collections of macrophages and eosinophils may be seen in vascular spaces. Note the presence of eosinophils, not only inside the vessels, but in addition in adjoining tissue. Multinucleated Giant Cells Interstitial Fibrosis (Left) this higher magnification shows the collections of macrophages and the obvious presence of multinucleated giant cells. This is considered one of the most important histopathological options of hard metal pneumonitis. A few distorted airspaces are present (bottom) and a small bronchiole is present at the center of the sphere. Asbestos Bodies in Alveolar Lumina Ferruginous Bodies (Left) Cluster of ferruginous our bodies (asbestos particles) is seen in a sophisticated case of pulmonary asbestosis with advanced interstitial fibrosis. The structures have a rusty yellowish color because of the coating with an iron protein coat. Bhattacharjee P et al: Risk of occupational publicity to asbestos, silicon and arsenic on pulmonary issues: Understanding the genetic-epigenetic interplay and future prospects. However, the identification of asbestos our bodies helps to establish the analysis of asbestos-related pulmonary fibrosis. Interstitial Fibrosis, High Power Interstitial Fibrosis Due to Asbestos (Left) this lung biopsy specimen reveals in depth areas of fibrosis with collections of pigmented macrophages within airspaces. Residual Airspaces Area of Severe Interstitial Fibrosis (Left) Closer view exhibits marked interstitial fibrosis with entrapment of residual alveolar lining. These options are indistinguishable from other interstitial fibrotic lung illnesses and, within the absence of asbestos our bodies, may be confused for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Note the presence of a pleural plaque, which consists basically of dense hyaline matrix.

Discount diltiazem 180mg with visa
Not all types of thymic carcinoma stain for this marker, and many other kinds of nonthymic cancers can be constructive as nicely. Low-Grade Neuroendocrine Carcinoma Pseudoglandular Pattern (Left) Low-grade neuroendocrine carcinoma exhibits areas of a pseudoglandular sample. The presence of mitosis and necrosis are important to determine the grade of the tumor. Mucinous Neuroendocrine Carcinoma Cystic Neuroendocrine Carcinoma (Left) Well-differentiated neuroendocrine carcinoma is proven with distinguished mucinous changes within the stroma. Clear Cell Neuroendocrine Carcinoma Angiomatoid Neuroendocrine Carcinoma (Left) Well-differentiated neuroendocrine carcinoma exhibits hanging clear cell options. Superimposed is the precise specimen resected from this affected person recapitulating the actual radiological imaging. Note the presence of hemorrhagic areas as well as focal necrotic areas, that are common findings in these tumors. Thymic Neuroendocrine Carcinoma Intermediate-Grade Neuroendocrine Carcinoma (Left) Low-power view of reasonably differentiated neuroendocrine carcinoma (atypical carcinoid) reveals evidence of comedo-like necrosis. Intermediate-Grade Neuroendocrine Carcinoma Oncocytic Intermediate-Grade Neuroendocrine Carcinoma (Left) Moderately differentiated neuroendocrine carcinoma (atypical carcinoid) reveals oncocytic modifications and mitotic exercise. The presence of mitotic activity is a vital feature for the grading of these tumors. Spindle Cell Intermediate-Grade Neuroendocrine Carcinoma 694 Neuroendocrine Carcinomas of Thymus Mediastinum: Neoplasms, Malignant, Primary Mucinous Neuroendocrine Carcinoma Sclerotic Neuroendocrine Carcinoma (Left) Mucinous neuroendocrine carcinoma is shown by which the mobile component is somewhat scant. The tumor is composed primarily of mucinous materials and fibroconnective tissue. Intermediate-Grade Neuroendocrine Carcinoma Chromogranin Stain (Left) Moderately differentiated neuroendocrine carcinoma (atypical carcinoid) shows a loss of the organoid pattern, and the tumor exhibits a disorganized sample of progress. However, it is important to keep in thoughts that chromogranin staining can also be optimistic in other neuroendocrine tumors. High-Grade Neuroendocrine Carcinoma High-Grade Neuroendocrine Carcinoma (Left) High-grade neuroendocrine carcinoma, small cell type, reveals a sheets of malignant cells. Subtle necrosis and nuclear molding are present, the same as when these tumors occur in the lung. Mature Epithelium Enteric Glands (Left) Mature teratoma is proven with focal necrotic area. In addition, the tumor exhibits mature enteric glands and different cystic buildings lined by mature epithelium. El Mesbahi O et al: Chemotherapy in sufferers with teratoma with malignant transformation. Pancreatic Tissue Dermal Tissue (Left) Mature teratoma shows acinar buildings suitable with pancreas. Pancreas is a typical element in mediastinal teratomas, and, in some instances, it could be a functioning pancreas. These structures are invariably present within the great majority of mature teratomas. Cartilage and Adipose Tissue Dermal Appendages (Left) Mature teratoma shows 2 traditional mature part in these tumors: Mature cartilage and mature adipose tissue. However, the presence of solid areas should be suspicious for immature or other malignant parts. Immature Teratoma Neural Structures (Left) Mediastinal immature teratoma exhibits outstanding solid areas with solely scattered tubular neural structures. Neural Rosettes Neural Rosettes and Cartilage (Left) Mediastinal immature teratoma is proven with neural rosettes admixed with cartilage. Immature Elements 700 Mediastinal Teratoma Mediastinum: Neoplasms, Malignant, Primary Macroscopic Features Yolk Sac Component (Left) Gross photograph reveals a mediastinal teratoma with a malignant part. Once again, the presence of stable areas should raise the suspicion of a attainable malignant component. Yolk Sac Tumor and Mature Elements Adenocarcinoma Component (Left) Closer view exhibits the yolk sac element of this teratomatous lesion. This type of teratoma corresponds to sort I, which is a teratoma associated with another germ cell tumor. In this case, the malignant part is adenocarcinoma, a malignant epithelial component. In some circumstances, the malignant mesenchymal element could also be of the undifferentiated kind.
Cheap diltiazem
On cursory examination, the sheets of cells could be confused for a malignant course of. Notice the clear halo surrounding the inclusion and the accentuation of the nuclear membrane. The presence of "smudge cells" (eosinophilic inclusions filling the nucleus) is distinctive for adenovirus. Viral Particles Cowdry Inclusion (Left) Cowdry kind A intranuclear eosinophilic inclusion in adenovirus pneumonia reveals a characteristic clear halo, separating it from the nuclear envelope. Interstitial Pneumonia-Like Pattern Scattered Giant Cells (Left) Lung parenchyma exhibits the presence of an inflammatory reaction and the presence of a quantity of multinucleated giant cells. Acute Inflammation and Giant Cells Multinucleated Giant Cells (Left) Higher magnification of big cell interstitial pneumonia in a affected person with measles exhibits numerous big cells with multiple nuclei. The nuclei of the large cells characteristically wrap across the alveolar walls and surround the inflammatory cells within the lumen. Viral Pneumonia Multinucleated Giant Cells (Left) Higher magnification of a giant cell in measles interstitial pneumonia exhibits a number of small nuclei and scattered intracytoplasmic and intranuclear inclusions. Intranuclear Inclusions 526 Measles Pneumonia Lung: Infectious Diseases Squamous Metaplasia Atypical Squamous Epithelium (Left) Scanning magnification of the lung in a affected person with measles pneumonia reveals extreme acute and persistent irritation of a bronchus with intensive squamous metaplasia of the bronchial lining mucosa. The islands of squamous metaplasia are surrounded by continual irritation primarily composed of a mononuclear cell infiltrate. Inflammation and Giant Cells Acute Inflammation (Left) Section of lung in a affected person with pulmonary involvement by measles pneumonia shows necrotizing bronchiolitis with in depth destruction of the bronchiolar mucosa. Notice a number of scattered multinucleated giant cells distributed throughout the adjoining parenchyma. Edema and Inflammation Hyaline Membrane (Left) Acute lung injury in a patient with measles pneumonia reveals edema and congestion of alveolar septa with dense mononuclear cell inflammatory infiltrates. The alveolar lumina include edema fluid and scattered inflammatory cells and are lined by a skinny layer of dense eosinophilic material similar to that seen in diffuse alveolar damage. Granulomatous Inflammation Multinucleated Giant Cells (Left) Pulmonary sporotrichosis reveals acute inflammatory modifications and granulomatous irritation with numerous multinucleated giant cells. These features, though not pathognomonic of Klebsiella pneumonia, are suggestive. Acute Pneumonia Acute Pneumonia (Left) Higher magnification of Klebsiella pneumonia shows marked acute inflammatory infiltrate filling the alveolar spaces. Melot B et al: Bacteremic community-acquired infections as a result of Klebsiella pneumoniae: clinical and microbiological presentation in New Caledonia, 2008-2013. These features, though not specific for Klebsiella pneumonia, should immediate using cultures and special stains. Fibrinous Exudate Abscess Formation (Left) Klebsiella pneumonia reveals abscess formation throughout the airway, while the adjoining lung parenchyma shows congestion and inflammatory modifications. Acute Inflammation Acute Pneumonia (Left) Klebsiella pneumonia reveals in depth areas of fibrinous component admixed with acute inflammatory cells. The course of is clearly infectious and requires using cultures and particular histochemical stains for identification of the organism. In this case, the acute inflammatory cells are admixed with fibrin, leaving only some recognizable structures, corresponding to pulmonary vessels. Note the presence of abscess formation and the destruction of the adjacent regular lung parenchyma. Bronchial Erosion Alveoli With Acute Inflammatory Cells (Left) Klebsiella pneumonia involving major bronchi reveals erosion and destruction of the traditional mucosa and the presence of abscess formation. Gogna A et al: Severe acute respiratory syndrome: eleven years later-a radiology perspective. The remaining parts of the lung show acute inflammatory changes and a small growing abscess. Acute Pneumonia Positive Gram Stain (Left) Gram histochemical stains present quite a few filamentous bacterial organisms embedded in a pulmonary abscess. Abscess With Organism Actinomyces Organism (Left) High-power view of actinomycosis embedded in an abscess exhibits the presence of the purple shade of the organism and the characteristic granular look. The areas of infarction brought on by the occlusion of vessels might finally lead to cavitation adopted by the development of fungus balls.
Real Experiences: Customer Reviews on Diltiazem
Yasmin, 42 years: Cystic-Like Spaces Intraalveolar Macrophages (Left) Lipoid pneumonia shows some preservation of lung architecture by which the alveoli are crammed with histiocytes with focal areas of inflammatory response composed of lymphocytes. Alternate flaps for tongue defect reconstruction embody the lateral arm free flap. It is given orally for dietary purposes, however intravenously in critical emergencies. Note that while the villi are absent, the general thickness of the mucosa stays the identical.
Hamil, 65 years: This has usually been referred to as the patternless sample of development in these tumors. This cord-like arrangement of tumor cells is kind of distinctive and highly attribute of those tumors. The abdomen is explored for further proof of metastatic illness with explicit attention to the small bowel and mesentery. Currently used low dose pills with lipid pleasant progestin has received very minimum unwanted effects.
Brant, 26 years: Presence of mural nodules, papillary excrescence, solid components recommend malignancy. Injections of repeated boluses of glucose resolution 35 % in addition to iv infusions of 10 or 20 % glucose resolution are carried out. Note the presence of the attribute tubular buildings across the fibrinoid areas of necrosis. Focal Fibrotic Areas Glandular Proliferation (Left) Endometrioid adenocarcinoma shows a malignant glandular proliferation in which the malignant glands are separated by thin fibroconnective tissue.
8 of 10 - Review by Y. Vandorn
Votes: 290 votes
Total customer reviews: 290
References
- Mayberg HS, Silva JA, Brannan SK, et al. The functional neuroanatomy of the placebo effect. Am J Psychiatry. 2002;159(5):728-737.
- Gnaho A, Eyrieux S, Gentili M. Cardiac arrest during an ultrasound-guided sciatic nerve block combined with nerve stimulation. Reg Anesth Pain Med 34:278, 2009.
- Paczynski RP. Osmotherapy: basic concepts and controversies. Crit Care Clin. 1997;13(1):105-29.
- DeFouw NJ, van Hinsbergh VW, deJong YF, et al: The interaction of activated protein C and thrombin with the plasminogen activator inhibitor released from human endothelial cells, Thromb Haemost 57:176, 1987.
- Schouten O, Bax JJ, Dunkelgrun M, et al: Statins for the prevention of perioperative cardiovascular complications in vascular surgery, J Vasc Surg 44:419-424, 2006.
- Maher J, Grand'maison F, Nicolle MW, Strong MJ, Bolton CF. Diagnostic difficulties in myasthenia gravis. Muscle Nerve. 1998;21:577-583.
- Haas JE, Muczynski KA, Krailo M, et al. Histopathology and prognosis in childhood hepatoblastoma and hepatocarcinoma. Cancer. 1989;64:1082-1095.